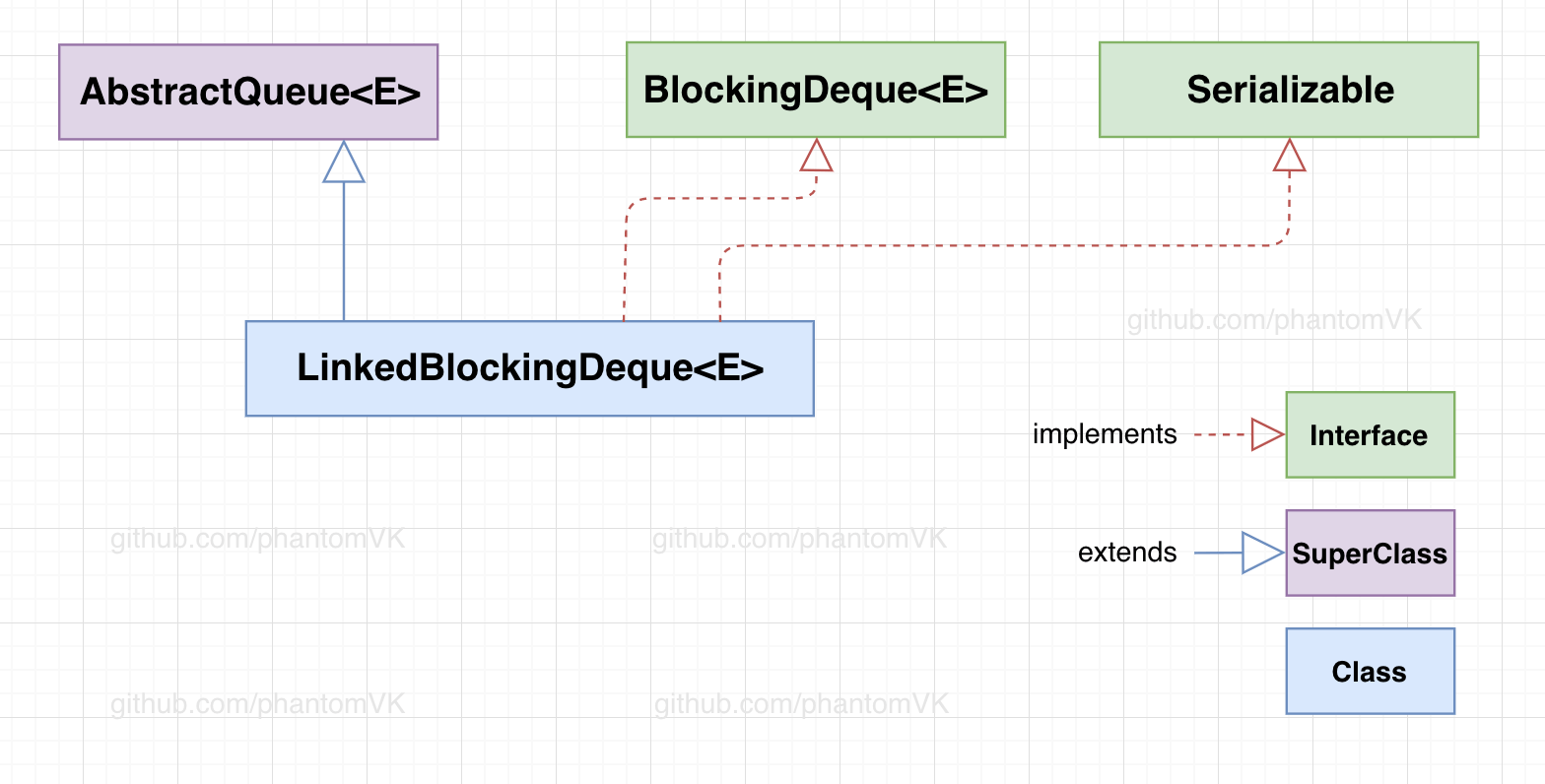
一、类签名
本类是基于链节点的、可选边界的阻塞双端队列。指定可选的容量避免队列过度扩展。
1
2
3
public class LinkedBlockingDeque<E>
extends AbstractQueue<E>
implements BlockingDeque<E>, java.io.Serializable
如果构造方法的容量参数没有指定,则 Integer.MAX_VALUE 将作为默认容量使用。而队列元素插入时,对应链节点动态创建。
多数操作能在常量时间内完成执行。例外的是 remove(Object)、removeFirstOccurrence 、removeLastOccurrence、 contains、iterator.remove() 和批量操作等方法,消耗的时间是线性的。源码来自JDK11
二、Node
双向链表的节点类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
static final class Node<E> {
// item,节点已被移除时为空
E item;
// 其一:
// - 真正的前导节点
// - 这个节点,表明前导节点是尾节点
// - null,表明没有前导节点
Node<E> prev;
// 其一:
// - 真正的后继节点
// - 这个节点,表明后继节点是头节点
// - null,表明没有后继节点
Node<E> next;
// 构造方法
Node(E x) {
item = x;
}
}
三、数据成员
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
// 指向队列首节点
// Invariant: (first == null && last == null) || (first.prev == null && first.item != null)
transient Node<E> first;
// 指向队列尾节点
// Invariant: (first == null && last == null) || (last.next == null && last.item != null)
transient Node<E> last;
// 双端队列已保存元素数量
private transient int count;
// 双端队列元素最大容量
private final int capacity;
// 保护所有访问操作的主锁
final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
// 等待获取的Condition
private final Condition notEmpty = lock.newCondition();
// 等待存入的Condition
private final Condition notFull = lock.newCondition();
四、构造方法
用 Integer.MAX_VALUE 构建实例
1
2
3
public LinkedBlockingDeque() {
this(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
用指定容量值构建实例
1
2
3
4
5
public LinkedBlockingDeque(int capacity) {
// 值小于1时抛出IllegalArgumentException
if (capacity <= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException();
this.capacity = capacity;
}
默认 Integer.MAX_VALUE 构建实例,且用指定集合的元素作为双端队列的初始元素
1
2
3
4
public LinkedBlockingDeque(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
addAll(c);
}
五、成员方法
5.1 link
把指定节点作为第一个元素存入,如果队列已满返回false
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
private boolean linkFirst(Node<E> node) {
// 检查容量是否已满
if (count >= capacity)
return false;
// 获取第一个节点
Node<E> f = first;
// 新节点作为原首节点的前导节点
node.next = f;
first = node;
// 处理尾引用
if (last == null)
last = node;
else
f.prev = node;
// 元素数量统计递增
++count;
// 通知其他线程取数据
notEmpty.signal();
return true;
}
把指定节点作为最后一个元素存入,如果队列已满返回false
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
private boolean linkLast(Node<E> node) {
// 检查容量是否已满
if (count >= capacity)
return false;
// 获取最后一个节点
Node<E> l = last;
// 新节点作为原尾节点的后继节点
node.prev = l;
last = node;
// 处理头引用
if (first == null)
first = node;
else
l.next = node;
// 元素数量统计递增
++count;
// 通知其他线程取数据
notEmpty.signal();
return true;
}
5.2 unlink
移除并返回第一个元素,如果为空则返回null
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
private E unlinkFirst() {
// 获取首节点
Node<E> f = first;
if (f == null)
return null;
// 首节点的下一个节点
Node<E> n = f.next;
// 获取首节点的item
E item = f.item;
// 清空首节点
f.item = null;
// 首节点的后继节点引用为自己
f.next = f;
// 处理头引用
first = n;
if (n == null)
last = null;
else
n.prev = null;
// 元素数量统计递减
--count;
notFull.signal();
// 返回首节点的内容
return item;
}
移除并返回最后一个元素,如果为空则返回null
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
private E unlinkLast() {
// 获取尾节点
Node<E> l = last;
if (l == null)
return null;
// 尾节点的上一个节点
Node<E> p = l.prev;
// 获取尾节点的item
E item = l.item;
// 清空尾节点
l.item = null;
l.prev = l;
// 处理尾引用
last = p;
if (p == null)
first = null;
else
p.next = null;
// 元素数量统计递减
--count;
notFull.signal();
// 返回尾节点的内容
return item;
}
从队列中移除x节点
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
void unlink(Node<E> x) {
Node<E> p = x.prev;
Node<E> n = x.next;
// p为空表示x是队列的首节点
if (p == null) {
unlinkFirst();
} else if (n == null) {
// n为空表示x是队列的尾节点
unlinkLast();
} else {
// x是队列的中间节点
p.next = n;
n.prev = p;
x.item = null;
// 不要置空x.next的节点,因为x节点在iterator里可能在使用
--count;
notFull.signal();
}
}
5.3 阻塞双端队列
两个 add 方法是 offer 方法的变体
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
public void addFirst(E e) {
if (!offerFirst(e))
throw new IllegalStateException("Deque full");
}
public void addLast(E e) {
if (!offerLast(e))
throw new IllegalStateException("Deque full");
}
public boolean add(E e) {
addLast(e);
return true;
}
public boolean offer(E e) {
return offerLast(e);
}
public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException {
putLast(e);
}
public boolean offer(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException {
return offerLast(e, timeout, unit);
}
// 默认移除并返回双端队列的头节点
public E remove() {
return removeFirst();
}
public E poll() {
return pollFirst();
}
public E take() throws InterruptedException {
return takeFirst();
}
public E poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
return pollFirst(timeout, unit);
}
// 获取双端队列的头节点,但是获取之后不会移除该节点
public E element() {
return getFirst();
}
public E peek() {
return peekFirst();
}
// 返回双端队列可用容量
// 不要通过观察队列剩余容量来确定元素成功插入,因为其他线程也可能在增加或移除元素
public int remainingCapacity() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
// 获取锁
lock.lock();
try {
// 计算剩余有效容量
return capacity - count;
} finally {
// 解锁
lock.unlock();
}
}
public int drainTo(Collection<? super E> c) {
return drainTo(c, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
public int drainTo(Collection<? super E> c, int maxElements) {
Objects.requireNonNull(c);
if (c == this)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
if (maxElements <= 0)
return 0;
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
// 获取锁
lock.lock();
try {
int n = Math.min(maxElements, count);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
c.add(first.item); // In this order, in case add() throws.
unlinkFirst();
}
return n;
} finally {
// 解锁
lock.unlock();
}
}
5.4 offer
存入元素为空则抛出NullPointerException
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
public boolean offerFirst(E e) {
// 存入元素不能为空
if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException();
// 把e封装为新Node
Node<E> node = new Node<E>(e);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
// 获取锁
lock.lock();
try {
return linkFirst(node);
} finally {
// 解锁
lock.unlock();
}
}
public boolean offerLast(E e) {
// 存入元素不能为空
if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException();
// 把e封装为新Node
Node<E> node = new Node<E>(e);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
// 获取锁
lock.lock();
try {
return linkLast(node);
} finally {
// 解锁
lock.unlock();
}
}
等待存入元素到队列头时被中断抛出 InterruptedException
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
public boolean offerFirst(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException {
// 存入元素不能为空
if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException();
// 创建新节点
Node<E> node = new Node<E>(e);
// 换算为纳秒
long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
// 获取锁,且锁可中断
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (!linkFirst(node)) {
if (nanos <= 0L)
return false;
nanos = notFull.awaitNanos(nanos);
}
return true;
} finally {
// 解锁
lock.unlock();
}
}
等待存入元素到队列尾时被中断抛出 InterruptedException
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
public boolean offerLast(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException {
// 存入元素不能为空
if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException();
// 创建新节点
Node<E> node = new Node<E>(e);
// 换算为纳秒
long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
// 获取锁,且锁可中断
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (!linkLast(node)) {
if (nanos <= 0L)
return false;
nanos = notFull.awaitNanos(nanos);
}
return true;
} finally {
// 解锁
lock.unlock();
}
}
5.5 put
阻塞存入元素,当队列已满没有空间存入新元素,以下两个方法会阻塞等待并通知,等待没有设置超时时间。
元素存到队列头部
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
public void putFirst(E e) throws InterruptedException {
// 存入元素不能为空
if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException();
// 把e封装为新Node
Node<E> node = new Node<E>(e);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
// 获取锁
lock.lock();
try {
while (!linkFirst(node))
notFull.await();
} finally {
// 解锁
lock.unlock();
}
}
元素存到队列尾部
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
public void putLast(E e) throws InterruptedException {
// 存入元素不能为空
if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException();
// 把e封装为新Node
Node<E> node = new Node<E>(e);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
// 获取锁
lock.lock();
try {
while (!linkLast(node))
notFull.await();
} finally {
// 解锁
lock.unlock();
}
}
5.6 remove
若双端队列为空,则抛出NoSuchElementException
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
public E removeFirst() {
E x = pollFirst();
if (x == null) throw new NoSuchElementException();
return x;
}
public E removeLast() {
E x = pollLast();
if (x == null) throw new NoSuchElementException();
return x;
}
5.7 poll
先获取线程锁,然后调用对应方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
public E pollFirst() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
return unlinkFirst();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public E pollLast() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
return unlinkLast();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
// 带超时的poll
public E pollFirst(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException {
long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
E x;
while ( (x = unlinkFirst()) == null) {
if (nanos <= 0L)
return null;
nanos = notEmpty.awaitNanos(nanos);
}
return x;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
// 带超时的poll
public E pollLast(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException {
long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
E x;
while ( (x = unlinkLast()) == null) {
if (nanos <= 0L)
return null;
nanos = notEmpty.awaitNanos(nanos);
}
return x;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
5.8 take
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
public E takeFirst() throws InterruptedException {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
E x;
while ( (x = unlinkFirst()) == null)
notEmpty.await();
return x;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public E takeLast() throws InterruptedException {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
E x;
while ( (x = unlinkLast()) == null)
notEmpty.await();
return x;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
5.9 get
若队列为空则抛出 NoSuchElementException
1
2
3
4
5
public E getFirst() {
E x = peekFirst();
if (x == null) throw new NoSuchElementException();
return x;
}
若队列为空则抛出 NoSuchElementException
1
2
3
4
5
public E getLast() {
E x = peekLast();
if (x == null) throw new NoSuchElementException();
return x;
}
5.10 peek
获取双端链表的头节点或尾节点,访问后不移出
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
public E peekFirst() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
return (first == null) ? null : first.item;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public E peekLast() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
return (last == null) ? null : last.item;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
5.11 removeOccurrence
移出第一个命中的指定元素。如果队列存在多个相同元素,每次调用方法仅移除一个元素。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
public boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o) {
if (o == null) return false;
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
// 顺序查找
for (Node<E> p = first; p != null; p = p.next) {
if (o.equals(p.item)) {
unlink(p);
return true;
}
}
return false;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
移出最后一个命中的指定元素。如果队列存在多个相同元素,每次调用方法仅移除一个元素。实现方式为倒序查找。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
public boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o) {
if (o == null) return false;
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
// 倒叙查找
for (Node<E> p = last; p != null; p = p.prev) {
if (o.equals(p.item)) {
unlink(p);
return true;
}
}
return false;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
5.12 栈方法
压栈,即向双端队列头部添加元素
1
2
3
public void push(E e) {
addFirst(e);
}
弹栈,即从双端队列头部移除节点
1
2
3
public E pop() {
return removeFirst();
}
5.13 Collection方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
// 移除双端队列第一次遇到的指定节点,若节点不存在返回false
public boolean remove(Object o) {
return removeFirstOccurrence(o);
}
// 返回双端队列已保存节点数量
public int size() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
return count;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
// 若双端队列包含指定元素返回true,即可队列保存多个相同元素,查找时命中了其中一个
public boolean contains(Object o) {
if (o == null) return false;
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
// 从队列头部元素开始遍历匹配目标元素
for (Node<E> p = first; p != null; p = p.next)
if (o.equals(p.item))
return true;
return false;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
// 把指定集合的元素全部添加到本双端队列尾部中,元素插入的顺序由c的迭代器决定
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
// 当插入集合和本实例是同一双端队列,抛出IllegalArgumentException
if (c == this)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
// 把c所有元素迁移到私有节点链
Node<E> beg = null, end = null;
int n = 0;
// 把c所有元素封装为Node,并连接到beg
for (E e : c) {
Objects.requireNonNull(e);
n++;
Node<E> newNode = new Node<E>(e);
if (beg == null)
beg = end = newNode;
else {
// end的后继节点是newNode
end.next = newNode;
// newNode的前导节点是end
newNode.prev = end;
// 尾引用从end移到newNode
end = newNode;
}
}
// 集合c没有元素,或里面的元素全为null
if (beg == null)
return false;
// 把元素原子性地插入到队列尾部中
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
// 获取锁
lock.lock();
try {
if (count + n <= capacity) {
beg.prev = last;
// 原队列为null
if (first == null)
// beg作为头结点
first = beg;
else
// 元素插入到队列尾部
last.next = beg;
// 更新尾引用
last = end;
// 更新队列元素总数量
count += n;
// 通知其他线程获取元素
notEmpty.signalAll();
return true;
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
// 当元素插入容量溢出导致IllegalStateException时,回到旧的非原子性的实现方法
return super.addAll(c);
}
5.14 toArray
返回包含双端队列所有元素的数组,元素顺序和双端队列元素顺序一致。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
s@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public Object[] toArray() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
// 创建新数组,大小为count
Object[] a = new Object[count];
int k = 0;
for (Node<E> p = first; p != null; p = p.next)
// 把队列的元素逐个放入数组中
a[k++] = p.item;
// 返回数组
return a;
} finally {
// 解锁
lock.unlock();
}
}
传入目标数组,并把双端队列所有元素放入该数组,元素顺序和双端队列元素顺序一致。返回数组的类型和传入数组类型相同。
如果传入数组大小不足容纳所有元素,方法会创建新数组,容量和所放入元素数量一致,放入所有元素后返回新数组。如果传入数组空间足够存入所有元素,该数组的下一个空间会被置为 null。
本方法可以实现队列转数组的功能:String[] y = x.toArray(new String[0]);。且值得注意的是,传入 toArray(new Object[0]) 和 传入 toArray() 效果完全相同。
传入 数组元素的运行类型,不是 本队列元素的运行类型 的子类时,抛出 ArrayStoreException。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
// 上锁
lock.lock();
try {
// 双端队列元素数量比指定数组空间大,则需要创建新数组并赋值给a
if (a.length < count)
// 新数组类型为a.getClass().getComponentType(),大小为count
a = (T[])java.lang.reflect.Array.newInstance
(a.getClass().getComponentType(), count);
// 初始数组索引k
int k = 0;
for (Node<E> p = first; p != null; p = p.next)
// 把队列的元素逐个放入数组中
a[k++] = (T)p.item;
if (a.length > k)
// 置空索引k的值
a[k] = null;
// 返回数组
return a;
} finally {
// 解锁
lock.unlock();
}
}
5.15 clear
原子性地从双端队列移除所有元素
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
public void clear() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
// 获取锁
lock.lock();
try {
for (Node<E> f = first; f != null; ) {
// 清空节点负载
f.item = null;
// 解除节点f的链接
Node<E> n = f.next;
// 清空前导引用
f.prev = null;
// 清空后继引用
f.next = null;
f = n;
}
first = last = null; // 头尾指针置空
count = 0; // 总元素数置0
notFull.signalAll();
} finally {
// 解锁
lock.unlock();
}
}
5.16 succ
不完全上锁的情况下进行元素遍历,此遍历需要应付以下两个问题:
- 已出队节点 (p.next == p)
- 多个内部的可能已移除的节点 (p.item == null)
1
2
3
4
5
Node<E> succ(Node<E> p) {
if (p == (p = p.next))
p = first;
return p;
}
5.17 checkInvariants
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
void checkInvariants() {
// assert lock.isHeldByCurrentThread();
// Nodes may get self-linked or lose their item, but only
// after being unlinked and becoming unreachable from first.
for (Node<E> p = first; p != null; p = p.next) {
// assert p.next != p;
// assert p.item != null;
}
}