一、类签名
LruCache是Android提供的缓存工具类,根据最近最少使用算法缓存元素,避免缓存导致内存占用过大,或对象释放不及时引起内存溢出。
1
public class LruCache<K, V>
被操作的元素会移到队列末位,一段时间后,原本处于队列末位的元素,因为其他元素的操作逐渐被挪动到队头。
如果队列空间足够,所有元素都不会移除。否则,处于队头的元素优先被移除,腾出空间容纳新元素。因此使用热度高的资源得到有效缓存,长时间没有使用的资源会被移出队列。
为了使该类适合实际应用,开发中多继承LruCache,重写create()、entryRemoved()和sizeOf()等方法。
二、数据成员
LruCache通过LinkedHashMap数据结构完成item的保存,传送门:LinkedHashMap源码阅读
1
private final LinkedHashMap<K, V> map;
以下两个数值分别用来记录保存容量及最大容量,且前者不大于后者。值得注意的是,这个容量可能是键的个数(针对Key),也可能是值总体积(针对Value)。
例如LruCache缓存图片,可以限制图片数量,或限制缓存图片总体积实现内存管理。
1
2
3
4
5
// 已保存数据大小
private int size;
// 最大数据可保存大小
private int maxSize;
统计所有操作次数,如:每次添加元素putCount递增。统计结果可作为性能优化的参考值。
1
2
3
4
5
private int putCount; // 加入
private int createCount; // 创建
private int evictionCount;// 舍弃
private int hitCount; // 查找命中
private int missCount; // 命中失败
三、构造方法
参数maxSize记录整个列表最大保存数。为避免严重的哈希冲突,默认哈希因子设定为0.75。
LinkedHashMap构造函数参数accessOrder为true时以访问顺序排列元素,否则以插入顺序排列元素为准。从源码可知LruCache的accessOrder为true。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
public LruCache(int maxSize) {
if (maxSize <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("maxSize <= 0");
}
this.maxSize = maxSize;
this.map = new LinkedHashMap<K, V>(0, 0.75f, true);
}
四、成员方法
LruCache作为一个二次封装LinkedHashMap类,在增删查改上提供有限但实用的方法。关键操作都是线程安全的,可放心在多线程操作LruCache实例。
4.1 设置大小
可以修改列表最大保存数量。如果maxSize变小,则通过trimToSize()移除多余元素。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
public void resize(int maxSize) {
if (maxSize <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("maxSize <= 0");
}
// 同步修改maxSize值
synchronized (this) {
this.maxSize = maxSize;
}
trimToSize(maxSize);
}
4.2 存取
通过非空键取值,对应键命中把值返回,且把这个元素移动到队列末位。
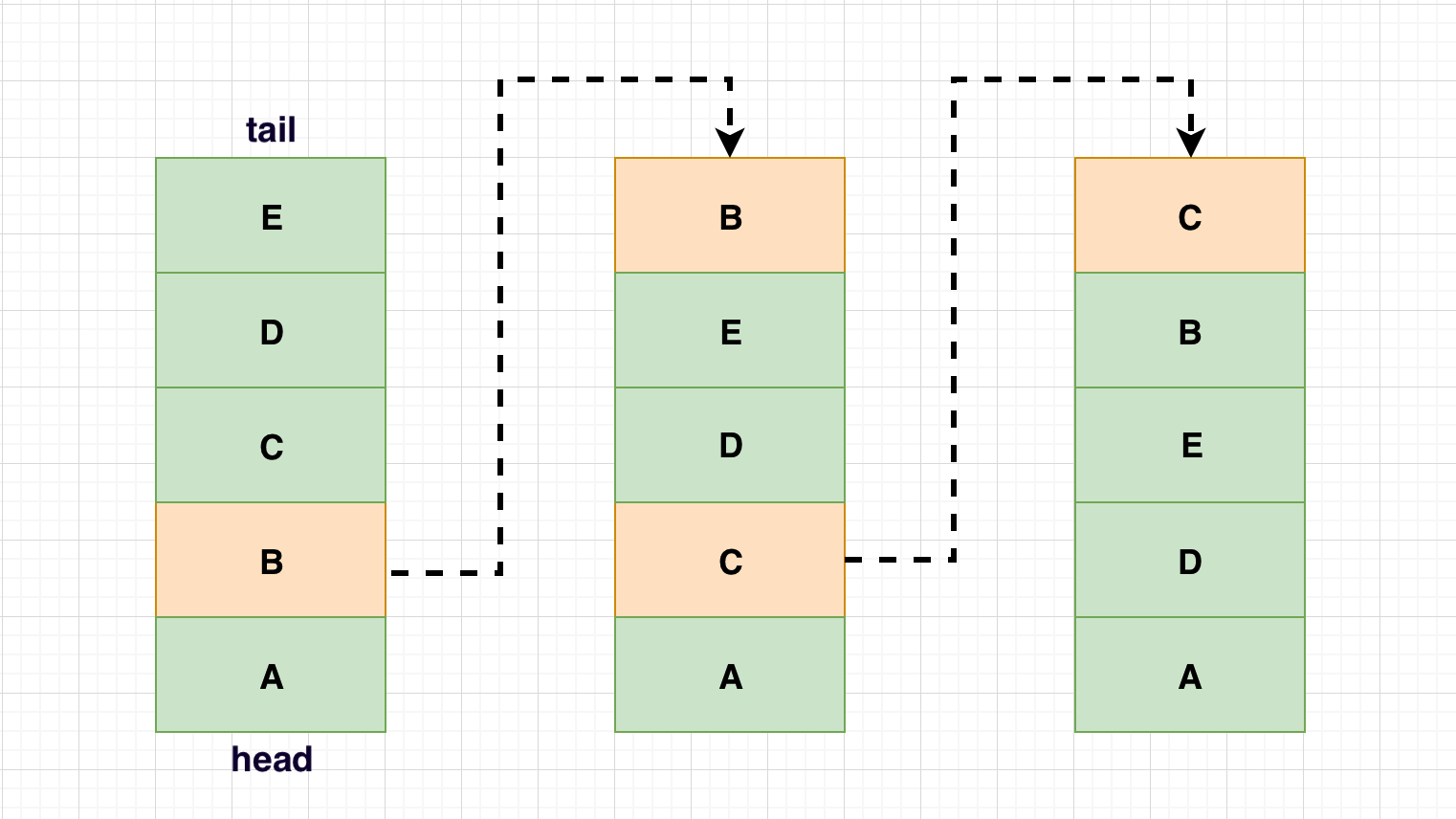
没有命中会根据create()做后续决定。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
public final V get(K key) {
if (key == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("key == null"); // 禁止使用空键取值
}
V mapValue;
synchronized (this) {
// 从LinkedHashMap中通过Key获取值
mapValue = map.get(key);
if (mapValue != null) {
hitCount++; // 命中对应值
return mapValue; // 返回命中值
}
missCount++; // 命中失败
}
// 命中失败后尝试构建Value
// 构建过程可能比较长,且当create()返回值时,原队列顺序可能已发生改变
// 若发现存在Key相同的item在队列中,该item会保留并抛弃create()的对象
V createdValue = create(key);
if (createdValue == null) {
return null;
}
synchronized (this) {
createCount++;
// 先用createdValue插入,并获得原位置旧值mapValue
mapValue = map.put(key, createdValue);
// 如果mapValue不为空,证明原位置有值
if (mapValue != null) {
// 把mapValue又替换回去,刚刚添加进去的createdValue又被换出来
// 相当于LruCache没有进行任何修改
map.put(key, mapValue);
} else {
// 没有冲突,新值成功插入,把新对象的大小加到总大小上
size += safeSizeOf(key, createdValue);
}
}
if (mapValue != null) {
// 两个实例出现冲突后把多余实例回收,这里是createdValue
entryRemoved(false, key, createdValue, mapValue);
return mapValue;
} else {
// 新值插入成功,且没有旧值被替换出来
// trimToSize()检查是否需要调整空间
trimToSize(maxSize);
return createdValue;
}
}
添加键值逻辑比较简单:已存在值会被新值替换且移到队列末位,旧值作为方法返回值。如果缓存没有满,则新值直接存入。
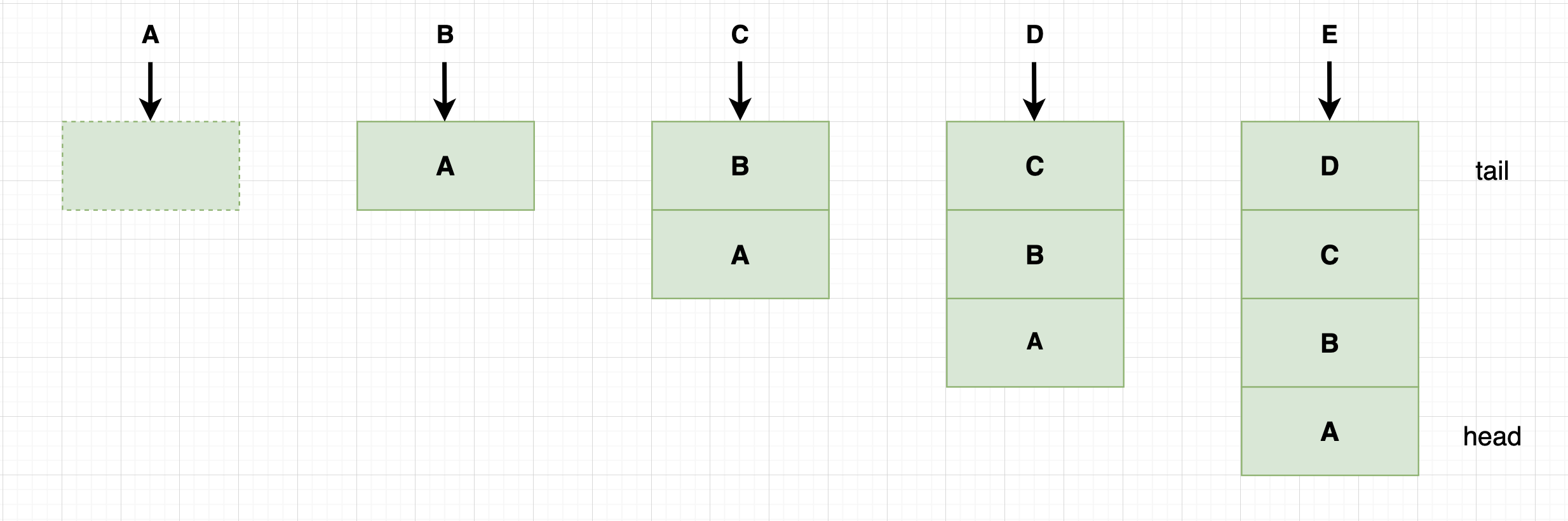
如果缓存已满,则先移除最旧一项数据再添加新值:
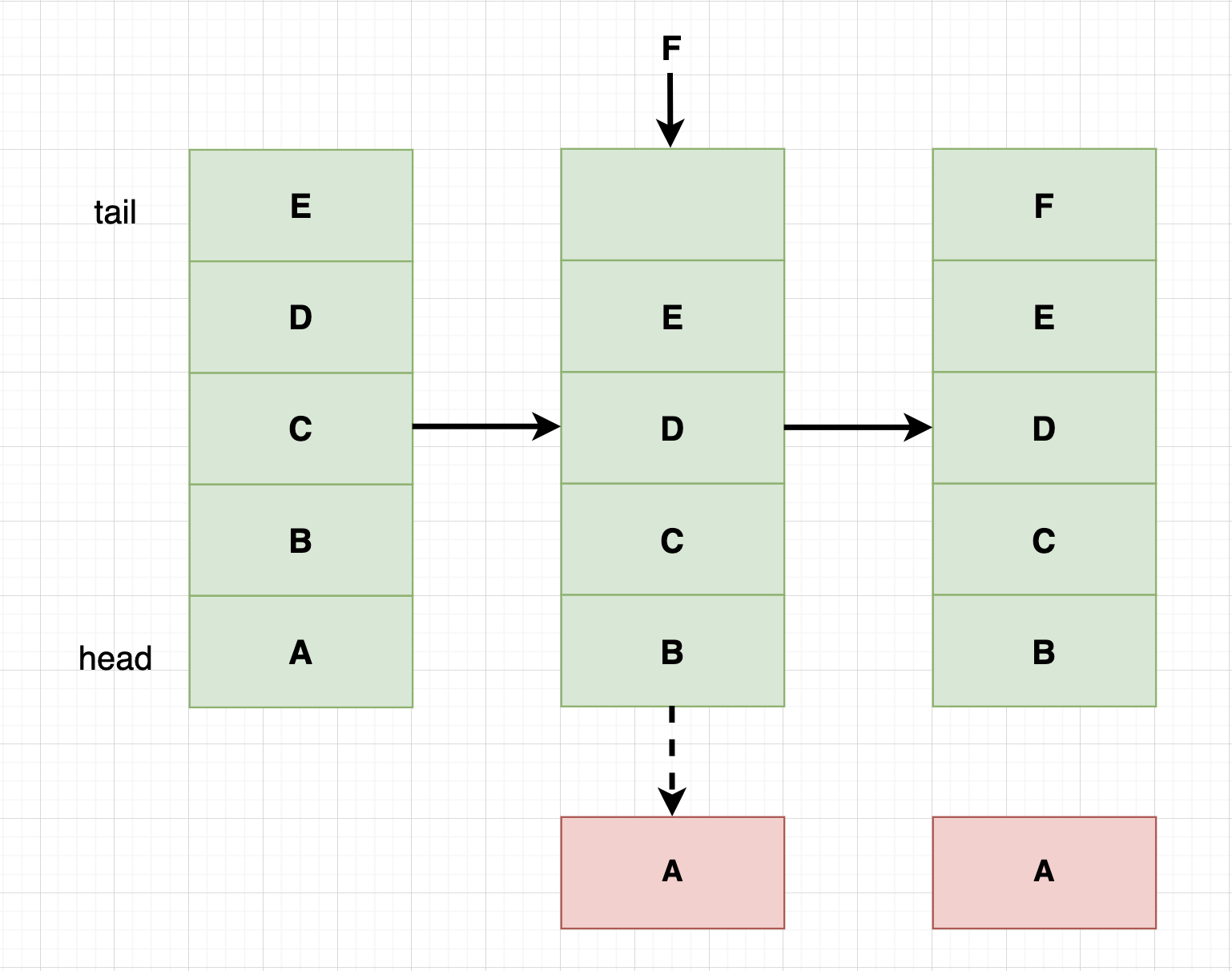
存入键值对:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
public final V put(K key, V value) {
if (key == null || value == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("key == null || value == null");
}
V previous;
synchronized (this) {
putCount++;
// 添加新元素,把新元素的大小增加到size
size += safeSizeOf(key, value);
// 被替换出来的元素
previous = map.put(key, value);
// 减去上一个元素空间占用
if (previous != null) {
size -= safeSizeOf(key, previous);
}
}
if (previous != null) {
// 执行移除操作
entryRemoved(false, key, previous, value);
}
// 调整大小
trimToSize(maxSize);
return previous;
}
4.3 调整容量
已保存元素数量大于新队列容量值,调整过程中选择近期最少使用的item出列。
下图把原长度从10裁剪为5,元素A到E被移除:
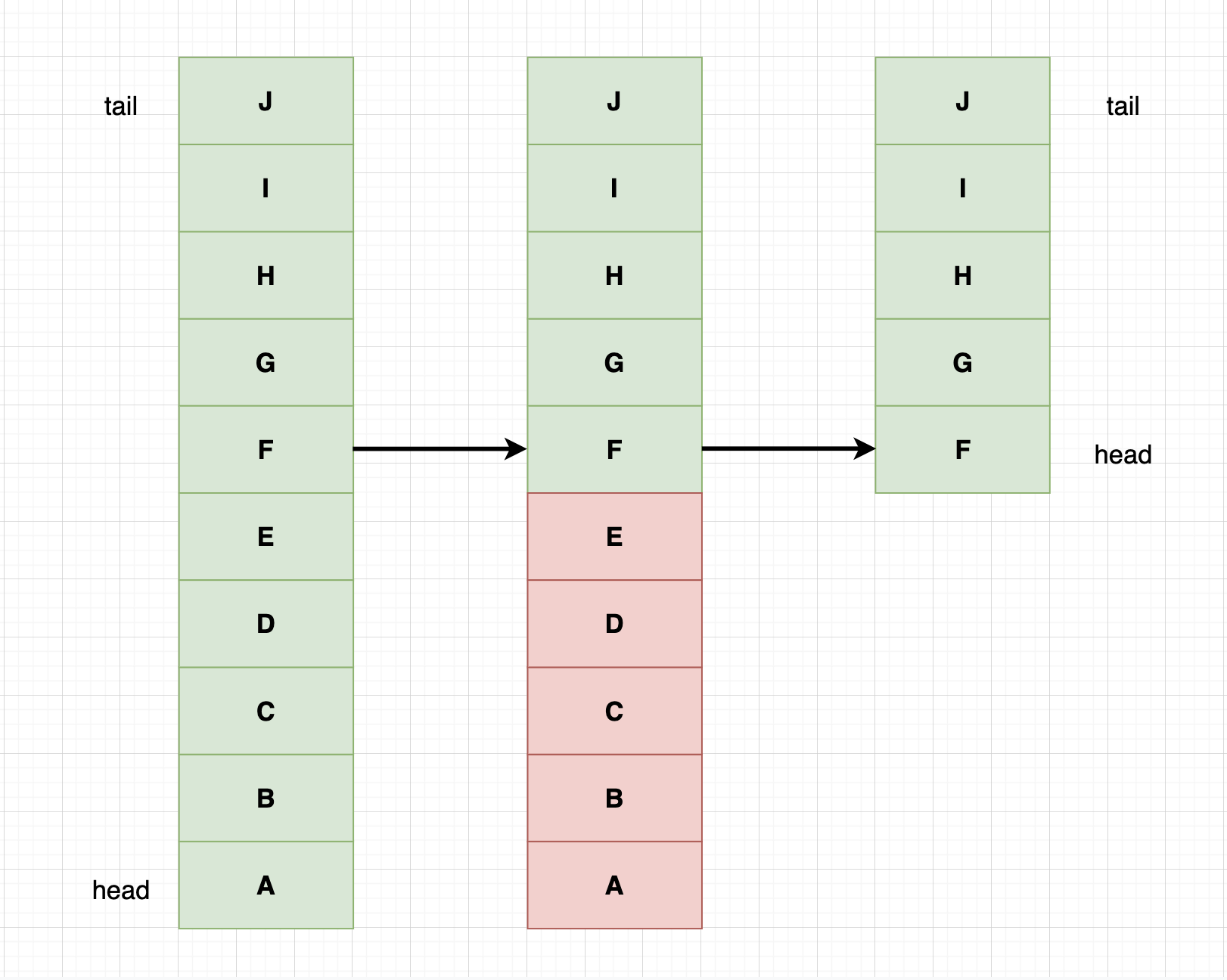
若maxSize值为-1,所有元素依次移除直至队列为空。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
public void trimToSize(int maxSize) {
while (true) {
K key;
V value;
synchronized (this) {
// 出现map的已保存元素数量和size值不对应,抛出异常
if (size < 0 || (map.isEmpty() && size != 0)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(getClass().getName()
+ ".sizeOf() is reporting inconsistent results!");
}
// 已保存size没有超过最大值,不需要移除旧元素
if (size <= maxSize) {
break;
}
// 获取最近最少使用元素,其实就是LinkedHashMap的头节点
// public Map.Entry<K, V> eldest() {return head;}
Map.Entry<K, V> toEvict = map.eldest();
// LinkedHashMap已空,退出清理
if (toEvict == null) {
break;
}
key = toEvict.getKey();
value = toEvict.getValue();
// 把该元素从LinkedHashMap中移除
map.remove(key);
// 调整总大小
size -= safeSizeOf(key, value);
evictionCount++;
}
entryRemoved(true, key, value, null);
}
}
4.4 移除键值
通过指定键移除元素
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
public final V remove(K key) {
// 键不能为空
if (key == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("key == null");
}
V previous;
synchronized (this) {
// 根据key在LinkedHashMap中查找元素
previous = map.remove(key);
// 元素成功移除,减去元素大小
if (previous != null) {
size -= safeSizeOf(key, previous);
}
}
if (previous != null) {
entryRemoved(false, key, previous, null);
}
return previous;
}
4.5 值创建和释放
4.5.1 entryRemoved()
有些类型的实例拥有独特回收逻辑,当实例被移出队列时,应该通过(需重写)此方法完成销毁操作。否则这个被移除的对象仅按照虚拟机垃圾回收策略进行回收。
1
protected void entryRemoved(boolean evicted, K key, V oldValue, V newValue) {}
要确定item是否有特殊释放需要,忽略释放操作可能会造成内存泄漏问题。
4.5.2 create()
在子类选择性重写此方法,目的是键值命中失败时把新建的item加入队列,默认返回null。
1
2
3
protected V create(K key) {
return null;
}
4.6 值大小
私有方法,对sizeOf()方法返回结果安全检查。假设item中存放的是Bitmap对象,需重写sizeof方法获取该对象占用内存大小。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
private int safeSizeOf(K key, V value) {
int result = sizeOf(key, value);
if (result < 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Negative size: " + key + "=" + value);
}
return result;
}
拿图片缓存为例:虽然可以控制图片在队列中缓存的数量,但却无法控制图片在内存中的占用。可能出现队列保存若干张图,每张图片占用多达16M内存,以至为数不多图片占用大量内存。
1
2
3
protected int sizeOf(K key, V value) {
return 1;
}
为此,折中的解决方案是计算图片内存占用,即使item依然保存在队列中,当内存占用超过阈值,也要强制释放队列LRU资源。当被释放图片后再次使用,应通过create(K key)重新加载。
默认值为1,表示元素占用一个单位。条目的size计算方法在运行时不能改变,否则会导致数量控制失效。